A rotating pink cam nudges the pawl forward, advancing the yellow gear by one tooth at a time.
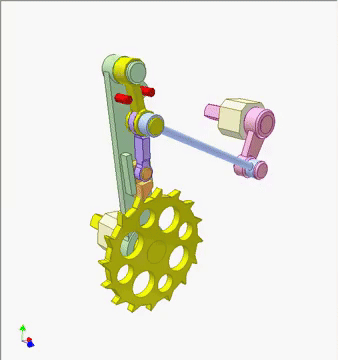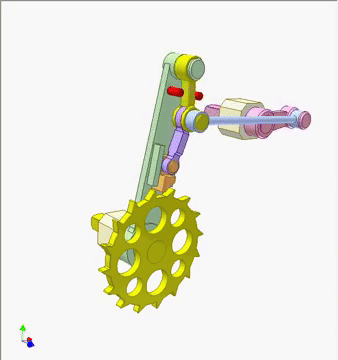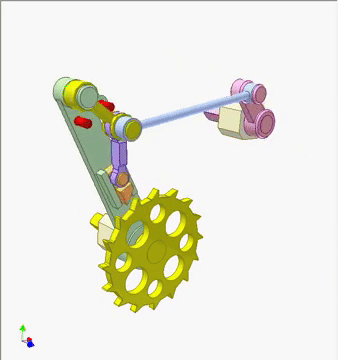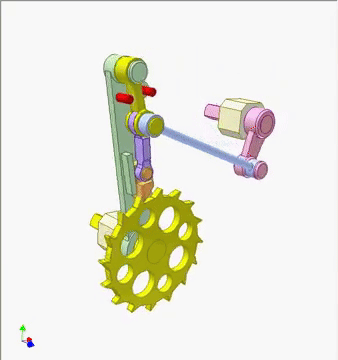
This mechanism uses a cam-driven pawl to create a smooth, incremental rotation of a ratchet wheel. As the pink cam turns, its profile rocks the slender linkage, which in turn pushes the pawl downward and forward. The pawl catches a tooth on the yellow ratchet wheel and advances it by a single step, while the return motion resets the pawl without pulling the wheel backward.
Components — Pink rotating cam, blue follower link, green frame, red guide pins, purple pawl linkage, yellow ratchet wheel, and return spring elements.
How it works — When the pink cam rotates, the follower link rises and falls according to the cam¡¯s contour, swinging the purple pawl arm in a controlled arc. As the pawl swings forward, its tip engages a tooth on the yellow ratchet wheel and pushes it ahead by one increment. On the return swing, the pawl tip lifts clear and slides over the next tooth, while the frame¡¯s fixed red stop prevents reverse rotation. Repeating this cycle converts continuous cam rotation into discrete, one-tooth advances of the ratchet wheel.
Applications — Indexing drives, measuring instruments, step-feed mechanisms, timing wheels, and devices requiring precise incremental rotation.
Why it matters — Cam-driven ratchets offer accurate, quiet stepping motion with excellent repeatability. Their geometry can be tuned for speed, force, and stroke, making them ideal for compact systems that need controlled rotation without complex electronics.
